Configuring DNS Anycast in Universal DDI (2577)
Scenario
We have DNS services running, but we want to make it highly available such that network clients communicate with a single IPv4 address that is always online and provides DNS service. This calls for DNS anycast configuration. Our team has decided to use the routing protocol BGP to provide DNS anycast service on the IPv4 address 10.24.7.53, served from NIOS-X servers oph1 and oph2.
Estimated Completion Time
20 to 30 minutes
Prerequisites
Administrative access to the Infoblox Portal
Tasks
Creating an anycast configuration for DNS.
Creating anycast service instances for NIOS-X servers oph1 and oph2.
Verifying the anycast service is online.
Verifying DNS service is working over anycast.
Task 1: Creating an anycast configuration
Create an anycast configuration for the DNS service, where we will define the anycast address that will be online as long as any one of the anycast nodes is reachable. Name this configuration Techblue DNS Anycast BGP with the anycast address 10.24.7.53.
Task 2: Configuring anycast service instance for oph1 and oph2
Create service instances and associate each to the anycast configuration we just created in Task 1. For each service instance, we will use the NIOS-X servers, oph1 and oph2, with the following values:
Table 2577-1
Service Instance | ASN | Keepalive | Hold Down | Neighbor Router | Remote ASN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Techblue Anycast Service 1 | 65400 | 4 | 16 | 10.100.0.1 | 65247 |
Techblue Anycast Service 2 | 65400 | 4 | 16 | 10.200.0.1 | 65247 |
Task 3: Verifying the anycast service is online
Before checking the DNS service, we must verify that the underlying anycast and BGP routes are working as intended. Verify that the anycast address 10.24.7.53 is reachable on the network and the appropriate BGP routes are present on the router. Optionally, simulate outages by shutting down NIOS-X servers one at a time to verify the address is highly available.
Task 4: Verifying DNS service is working over anycast
Finally, query the anycast address 10.24.7.53 to verify that we receive DNS responses.
Solutions
Task 1 Solution: Creating an anycast configuration
Log into your lab’s jump-desktop.
Use your Education Infoblox Portal Credentials to log into the Infoblox Portal.
In the Infoblox Portal, navigate to Configure → Networking → Anycast.
Click the button Create Anycast Configuration. This launches the Create Anycast Config dialog window.
Enter the following information:
Name: Techblue DNS Anycast BGP
Anycast IPv4 Address: 10.24.7.53
Service: DNS
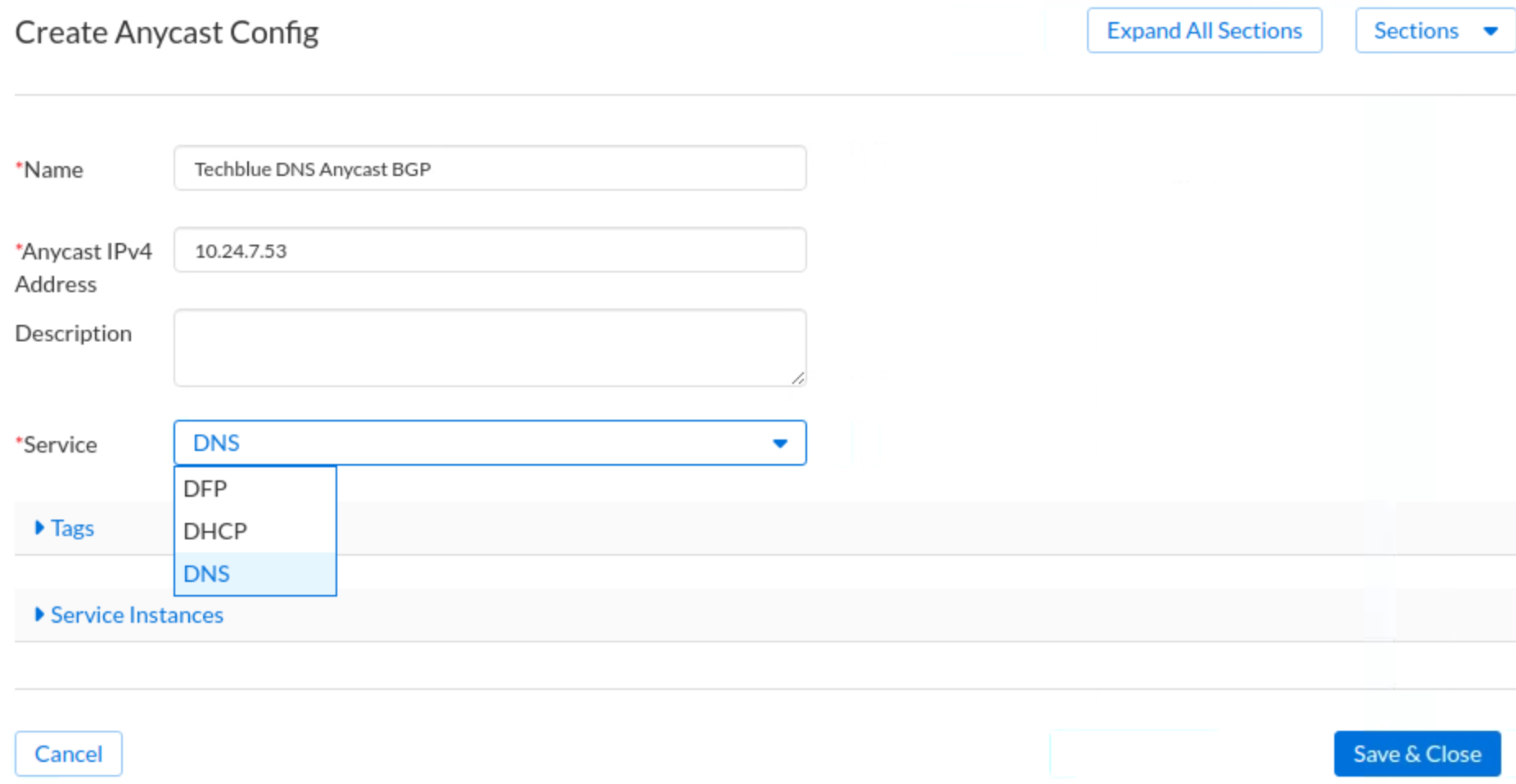
Click Save & Close.
Task 2 Solution: Creating anycast service instances for oph1 and oph2
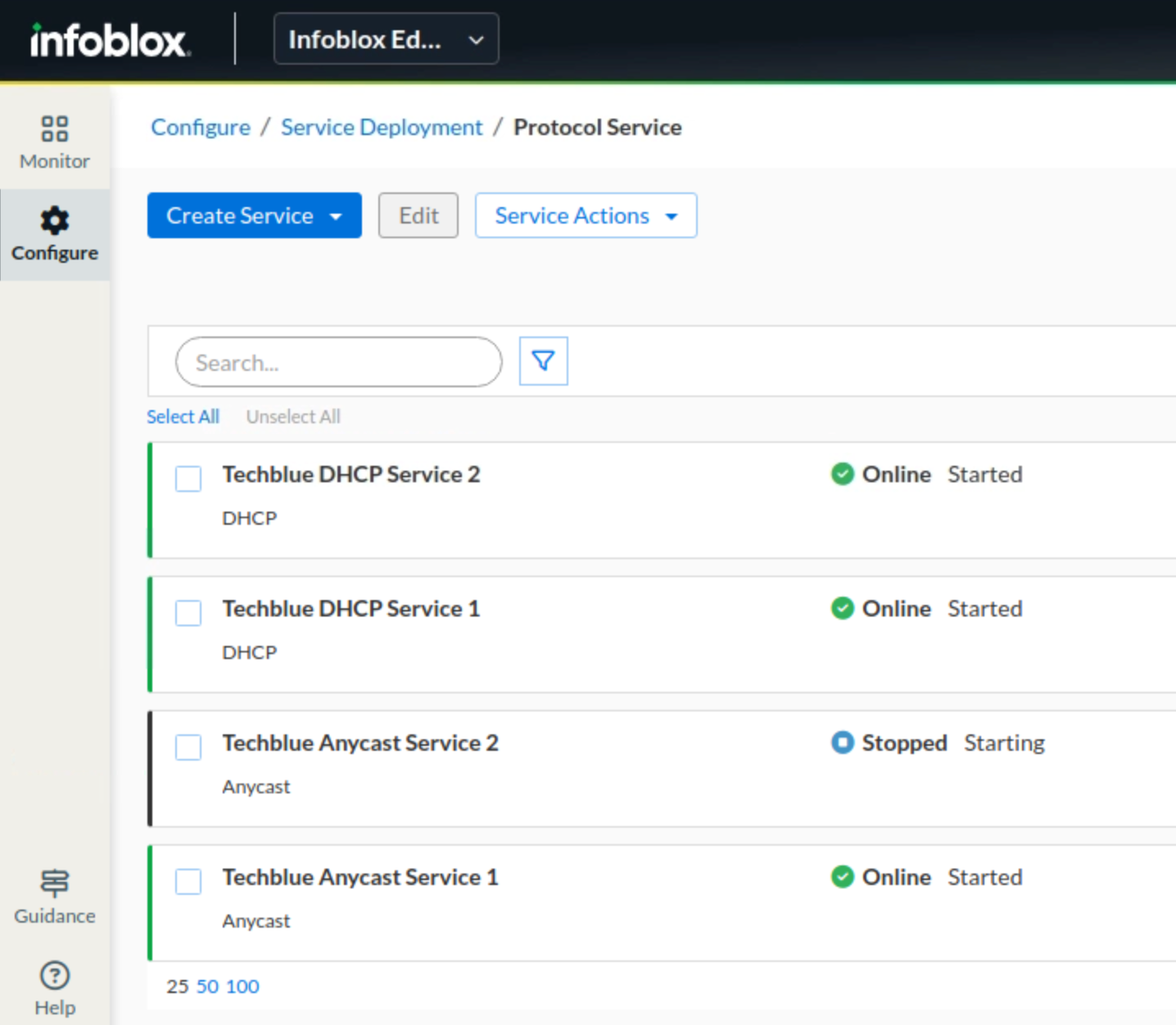
In the Infoblox Portal, navigate to Configure → Service Deployment → Protocol Service.
Click the button Create Service. From the drop-down list, select Anycast. This launches the Create Anycast Service dialog window.
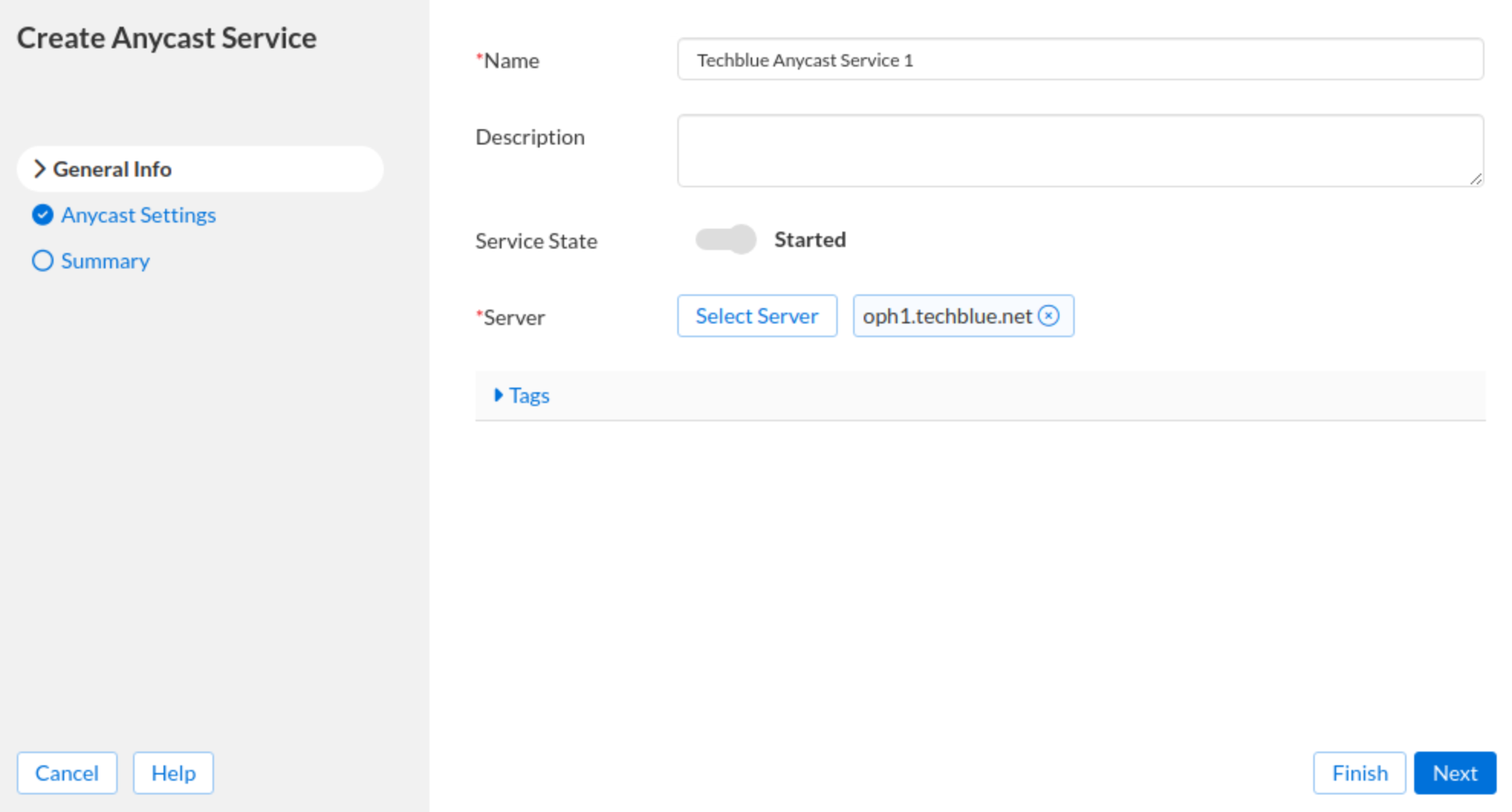
In the General Info tab, in the Name field, enter Techblue Anycast Service 1. Click Select Server, navigate to the server oph1.techblue.net, and click Select.
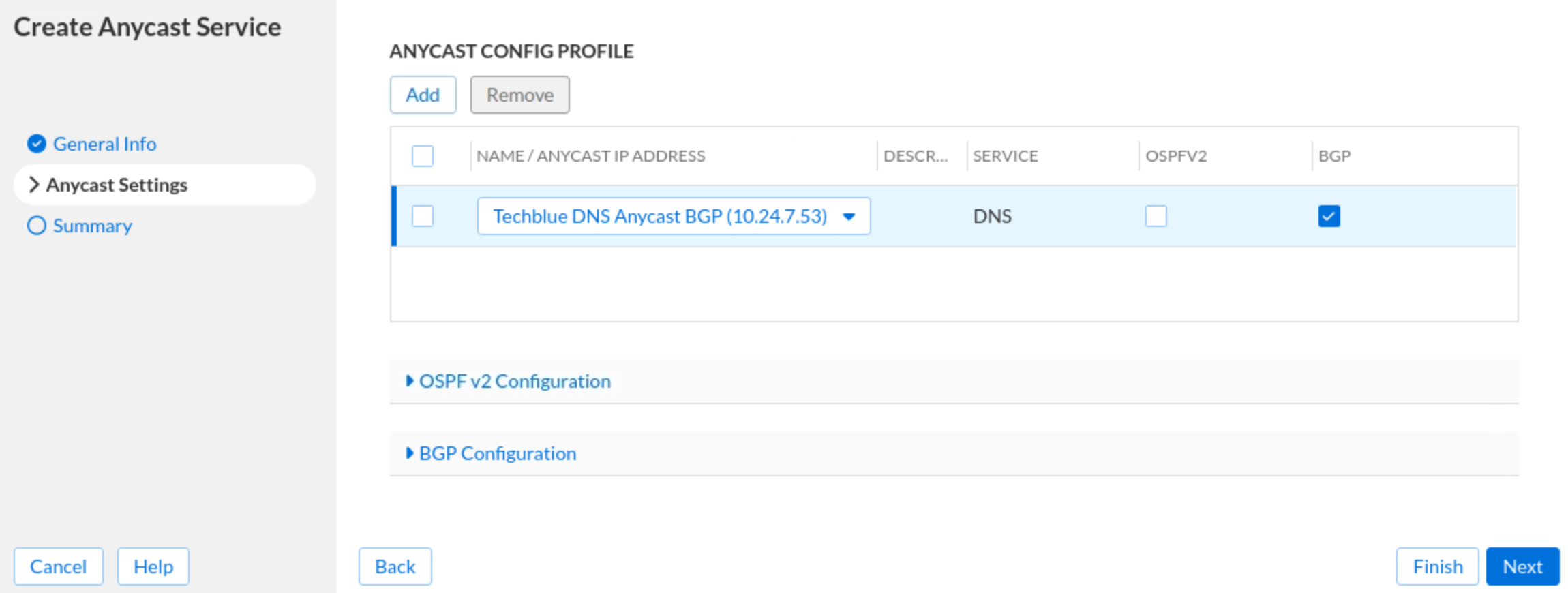
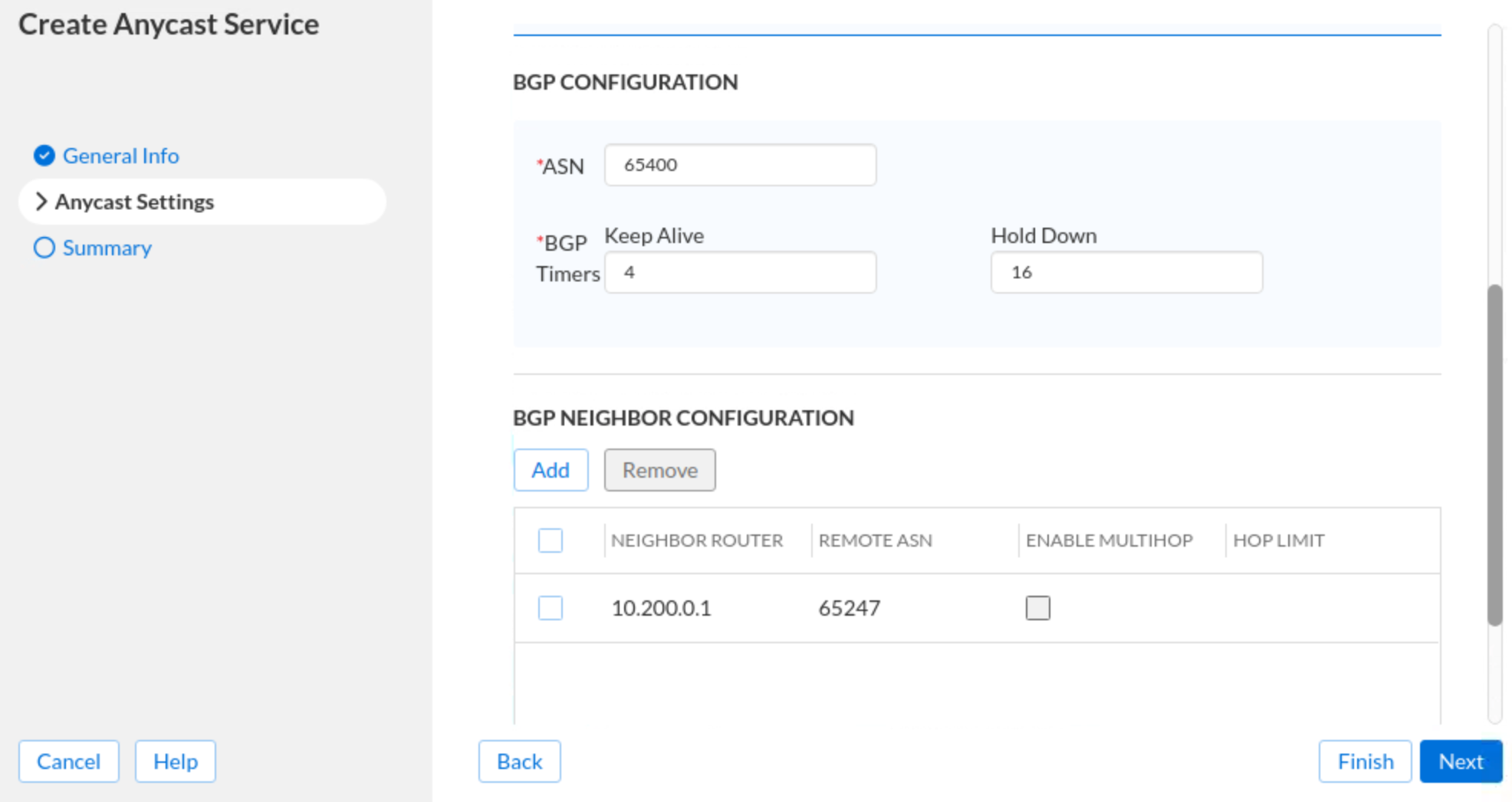
Click Next or the vertical tab Anycast Settings. Click Add in the ANYCAST CONFIG PROFILE section.
Select Techblue DNS Anycast BGP (10.24.7.53) from the drop-down, and tick the box for BGP.
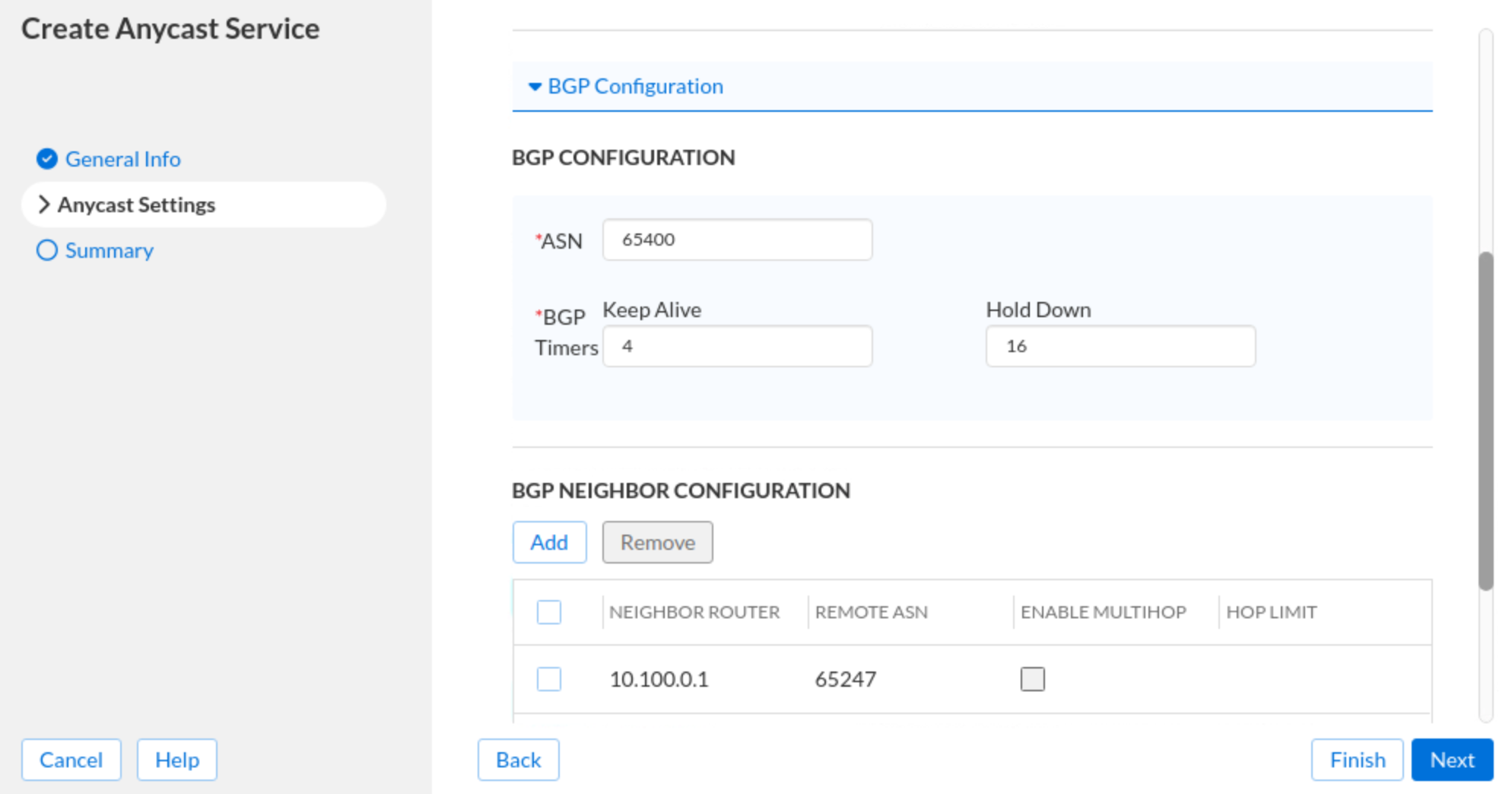
Scroll down and expand the BGP Configuration section and enter the following information:
ASN: 65400
BGP Timers: 4
Hold Down: 16
In the BGP NEIGHBOR CONFIGURATION section, click Add and provide the following information:
Neighbor Router: 10.100.0.1
Remote ASN: 65247
The configuration screen should appear as follows:
Click Next. A summary is displayed for oph1. Click Save & Close.
Repeat steps 2 through 9 to create an Anycast service instance for oph2 named Techblue Anycast Service 2. All configuration parameters are identical to oph1, except the neighbor router address is 10.200.0.1.
You may need to wait a few minutes for the Anycast services to start on both instances.
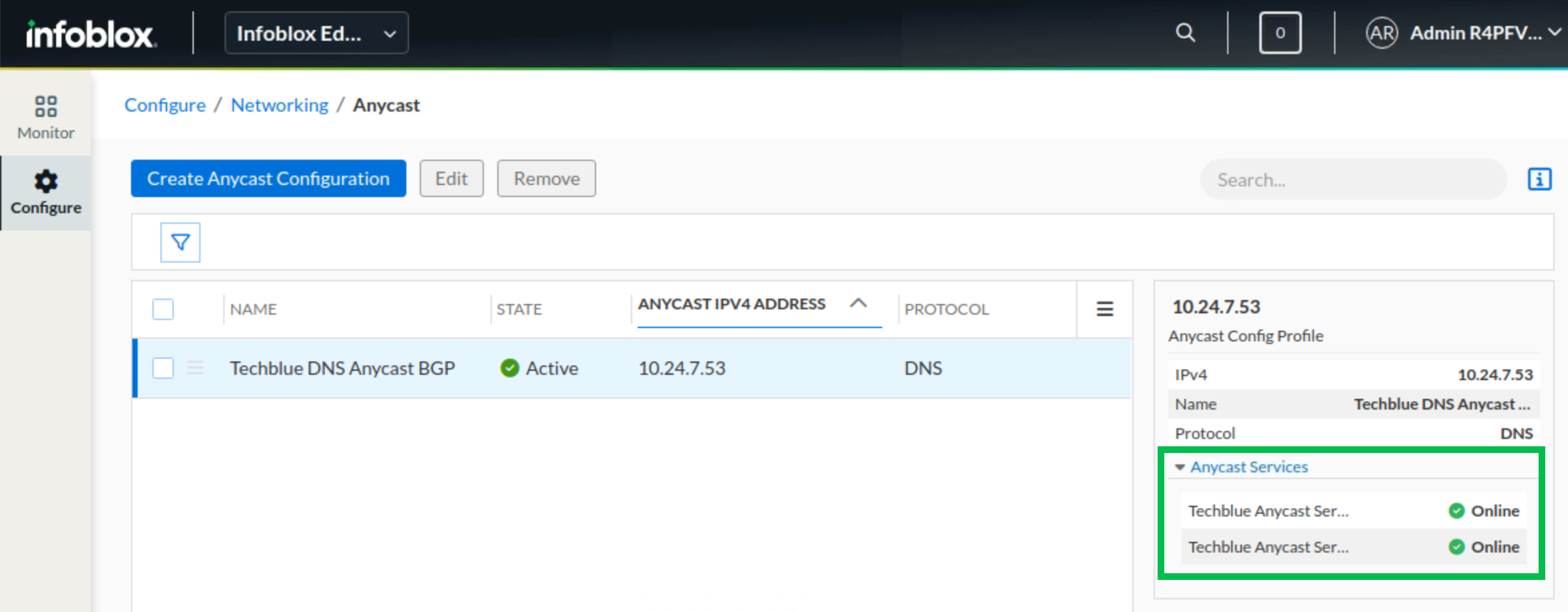
Task 3 Solution: Verifying the anycast service is online
In the Infoblox Portal, navigate to Configure → Networking → Anycast.
Check the status of the anycast configuration (what we created in Task 1). The status should be green and Active. To the right, we should see that both service instances are online.
We can further verify that the appropriate BGP routes have been propagated to the router by switching to the virtual machine vyos-router in the lab environment. (Both the login name and password are vyos)
Once logged in to the vyos-router, use the command
show ip bgpto see the list of routes. Look for the IP addresses of oph1 and oph2 (10.100.0.110 and 10.200.0.110).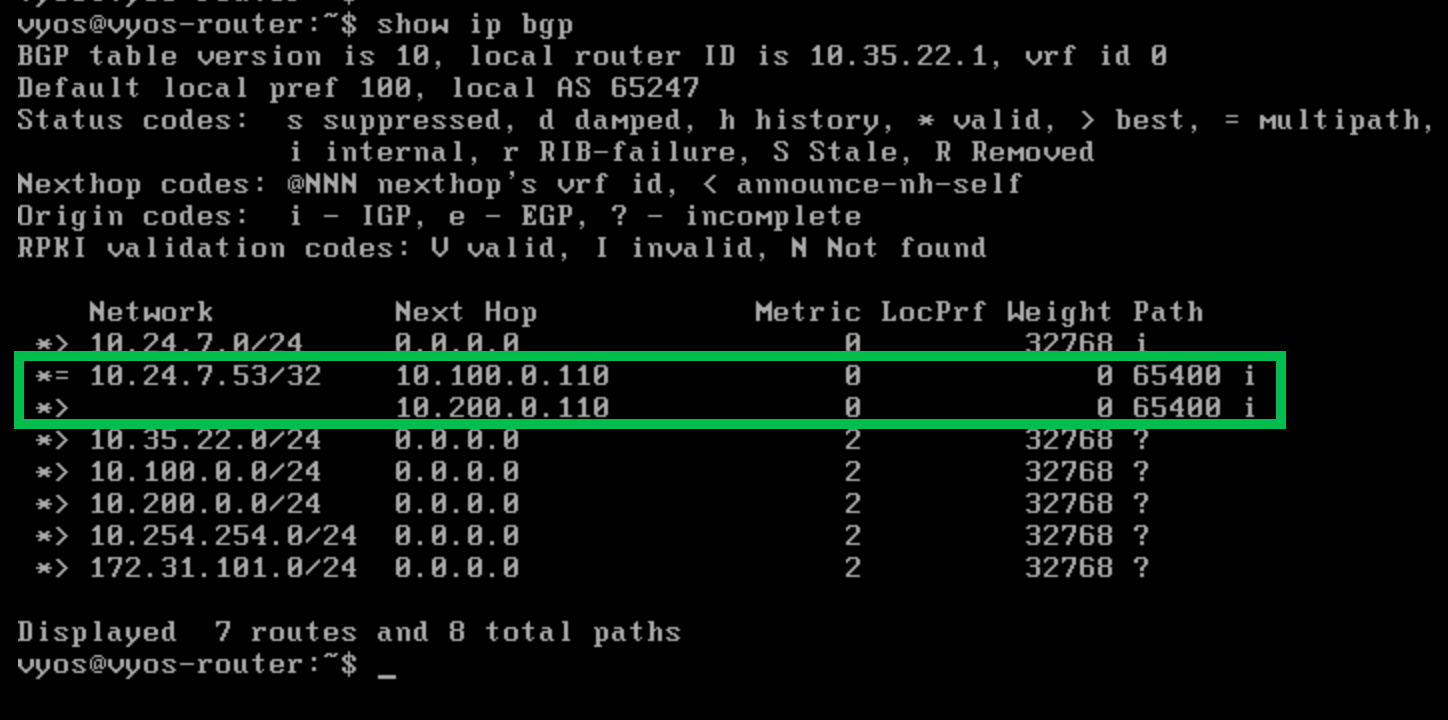
Switch to the virtual machine testing-linux and open a Terminal window.
Use the command
ping 10.24.7.53to verify that you can reach the anycast address.
You may simulate system failures by powering down the virtual machines oph1 and oph2, one at a time, while keeping the command
ping 10.24.7.53running. This verifies that anycast is working as intended, and that as long as one server is online, this IP address will respond on the network.
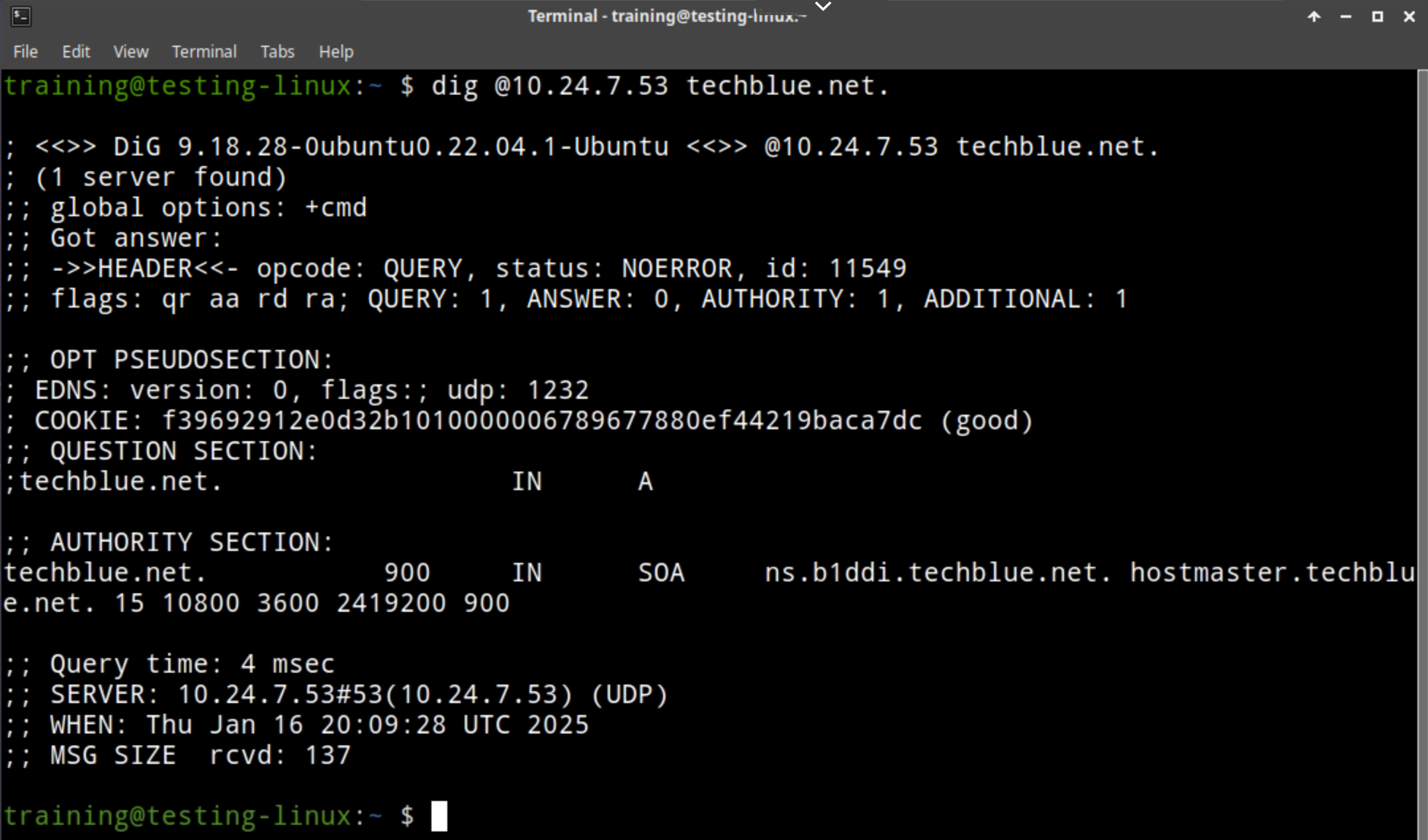
Task 4 Solution: Verifying DNS service is working over anycast
Switch to the virtual machine testing-linux and open a Terminal window.
Use the command
dig @10.24.7.53 techblue.net. This verifies that we can receive DNS responses from the anycast address.